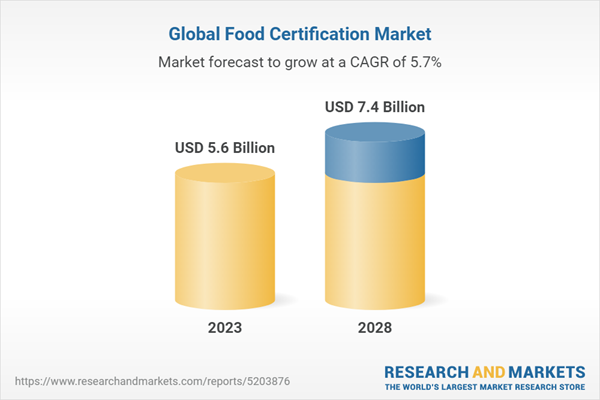
Global Food Safety Concerns Drive Record Food Certification
According to the CDC, Foodborne germs such as listeria monocytogenes, salmonella, toxoplasma gondii, norovirus and campylobacter are major causes of food poisoning, causing illness, hospitalizations and death. Ominously, many of these are increasingly antimicrobial resistant, meaning they are increasing resistant to the drugs developed to combat them.
Food traceability – the ability to record with precision the journey of food from farm to market and use that data to trace in real-time specific contaminated food back through all supply chain intermediaries to its farm source – is an essential tool to ensure food safety. Seem my recent article on the subject [“Listeria Outbreaks in US Food Supply Chain Highlights Need for Improved Food Traceability”].
But as this new report highlights, the certification that food meet – comply with – specific food harvesting, processing, storage and transportation regulations is an additional critical element in ensuring food safety. Each certification has its own requirements. To be effective, however, these compliance certifications must be diligently tracked without interruption from the source farm through all intermediaries to the consumer.
How Do Food Compliance Certifications Help Ensure Food Safety?
- Standardization: Certifications provide a standardized set of guidelines that producers, manufacturers, and suppliers can follow. This ensures that food safety measures are consistent across the industry.
- Verification and Validation: Certifications often require businesses to undergo regular inspections and audits. These checks verify that the processes being used adhere to the standards set by the certification body and validate that the food products are safe for consumption.
- Traceability: Many certifications emphasize the importance of traceability. This means that if a problem arises with a particular food product, it can be traced back to its source, making it easier to address and contain the issue.
- Training and Skill Development: To attain and maintain certification, companies often need to ensure their staff are adequately trained. This training covers best practices in food handling, processing, and storage, which directly contributes to improved food safety.
- Consumer Confidence: When consumers see that a product has been certified by a recognized body, they can have greater confidence in its safety. This puts pressure on businesses to maintain high standards and earn these certifications.
- Continuous Improvement: Many certification programs have a focus on continuous improvement. This means that over time, as new risks or challenges emerge, the standards will evolve and businesses will need to adapt to these changes, leading to an ongoing enhancement of food safety measures.
- Supply Chain Oversight: Certifications often look beyond just the final product. They consider the entire supply chain, ensuring that ingredients, additives, and even packaging materials meet rigorous safety standards.
- Access to Best Practices: Certification bodies often have access to the latest research and best practices in food safety. By aligning with these bodies, businesses can ensure they are using the most up-to-date and effective safety measures.
- Global Compatibility: For businesses involved in exporting and importing food products, having internationally recognized certifications ensures that their products meet the standards of different countries. This harmonization is crucial for maintaining safety in global trade.
- Legal and Regulatory Compliance: In many cases, having certain certifications can help businesses demonstrate that they are in compliance with local, national, or international regulations, thereby avoiding potential legal complications.
- Risk Management: Certifications help companies identify potential risks in their operations and provide guidelines on how to manage or eliminate those risks, thereby reducing the likelihood of food safety incidents.
About dFarm
dFarm’s Distributed ERP/SCM solutions track and certify adherence to all major agriculture industry quality compliances – including Organic, Kosher, Halal, HACCP, ISO 22000, Global GAP, BRC, SQF, FSSC, and IFS – through the entire value chain from farm to market, establishing quality trust that supports premium pricing by ensuring food meets the elevated quality consumers increasingly demand. dfarminc.com




